반응형
개념
전체 배열을 회문하며 가장 작은(큰) 원소를 찾아서 인덱스와 값을 기억한뒤,
현재 비교가 되고 있는 범위의 첫번째 원소와 값을 바꾼다.
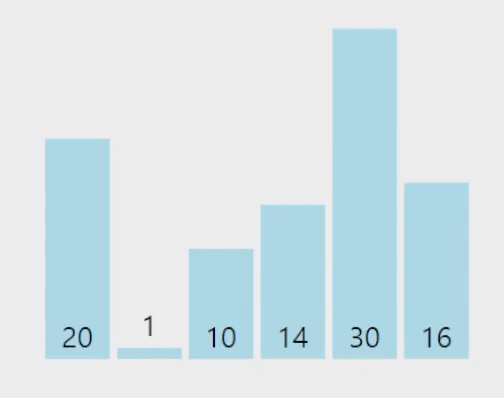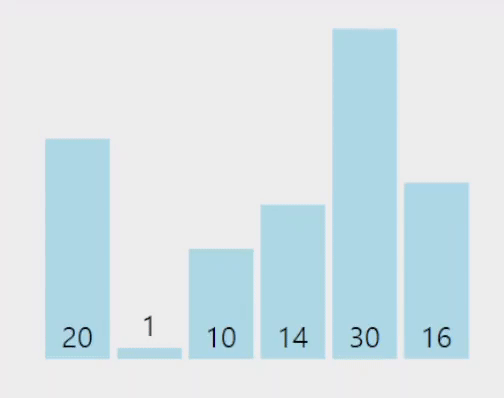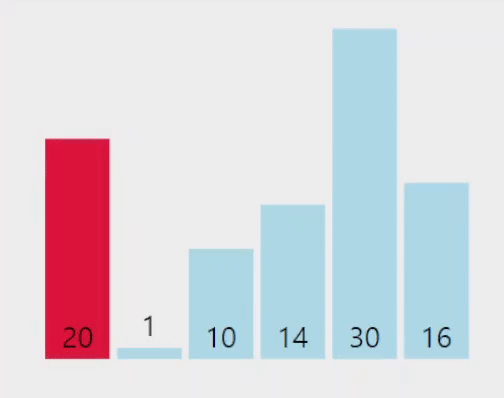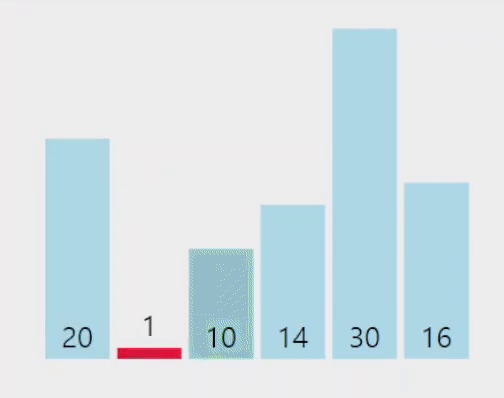
구현
const selectionSort = (inputArray) => {
for (let currentIndex = 0; currentIndex < inputArray.length; currentIndex++) {
for (let compareIndex = currentIndex + 1; compareIndex < inputArray.length; compareIndex++) {
if (inputArray[currentIndex] > inputArray[compareIndex]) {
let temp = inputArray[currentIndex];
inputArray[currentIndex] = inputArray[compareIndex];
inputArray[compareIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
return inputArray;
};
module.exports = selectionSort;선택정렬도 버블정렬과 동일하게 전체 배열의 길이 n만큼 반복하면서 현재 인덱스 다음 요소부터 끝까지 반복(n-1이라 표기하자)하므로 O(n^2)이다.
하지만 두번째 반복문의 범위가 계속해서 줄어듦으로, 버블정렬보다는 성능이 좋다고 할 수 있다.
테스트코드
이전의 버블정렬을 위해 사용한 테스트 코드를 활용해서 테스트해주자.
const 버블정렬 = require('../sort/bubbleSort');
const 선택정렬 = require('../sort/selectionSort');
const testData = [
{
testInput: [5, 3, 1],
testAnswer: [1, 3, 5],
},
{
testInput: [5, 3, 1, 5, 3, 22],
testAnswer: [1, 3, 3, 5, 5, 22],
},
{
testInput: [5, 3, 100, 1, 5, 99, 3, 22],
testAnswer: [1, 3, 3, 5, 5, 22, 99, 100],
},
{
testInput: [8, 9, 8, 8, 9, 8, 9],
testAnswer: [8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9],
},
{
testInput: [1, 9, 7, 8, 6, 8, 9],
testAnswer: [1, 6, 7, 8, 8, 9, 9],
},
];
const testFunction = [
버블정렬,
선택정렬
];
testFunction.forEach((func) => {
testData.forEach((testData, index) => {
test(`${func.name} 테스트 ${index}`, () => {
expect(func(testData.testInput)).toEqual(testData.testAnswer);
});
});
});반응형
